For a long time, “ambisonics” was predominantly considered as a way to create ambiences or record audio scenes and capture spatial aspects using a special type of microphone.
Today, we present ambisonics as an intermediate spatial representation instead, that allows binaural rendering for Virtual Reality (VR), all while avoiding the drawbacks of pure object-based audio.
Intermediate spatial representation for the purpose of binauralization
VR games need to render a binaural mix for headphones, produced by passing sounds through position-dependent filters called Head-Related Transfer Functions (HRTF). These filters model the interaction of sounds with the head, and can succeed in giving the impression that sounds of the game are actually coming from outside the player's head.
In order to apply proper HRTFs, binaural processing requires the direction of the arrival of sources. One way to do this is to filter each positioned source independently. However the operation of panning and applying binaural filtering source by source, has its drawbacks (see our previous post in this ambisonics series). In particular, it prevents sound designers from submixing groups of sounds for the purpose of applying audio Effects, such as dynamic range compression. To counteract these drawbacks, we need to decouple the panning stage with the binaural processing stage. In the middle, we need a signal format that carries some information about the spatiality of the sound constituting the submixed audio. We call this format an intermediate spatial representation, represented by the question marks in the figure below.
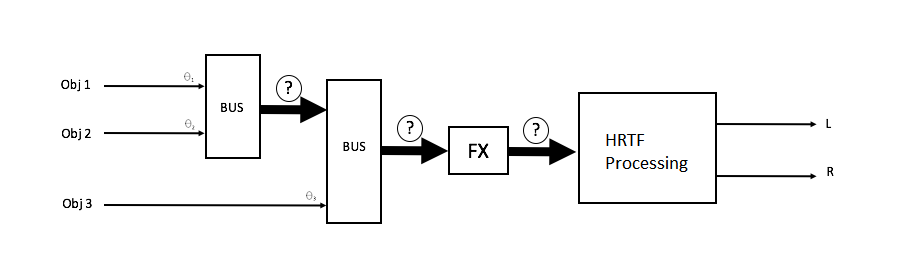 Figure 1 – Objects are submixed freely and panned onto a multichannel spatial audio representation which conveys the directional intensity of all its constituents and can also be manipulated by adding, for example, Effects.
Figure 1 – Objects are submixed freely and panned onto a multichannel spatial audio representation which conveys the directional intensity of all its constituents and can also be manipulated by adding, for example, Effects.
Compared with the binaural signal ensuing HRTF processing, which also carries information about space, the intermediate spatial representation is manipulatable; it can be exchanged and mastered, and is somewhat agnostic of the rendering environment (loudspeaker setup, or the set of HRTF).
"Virtual loudspeakers" representation
One suitable intermediate spatial representation uses virtual loudspeakers. The concept of virtual loudspeakers is quite simple. It consists of a multi-channel format, where each channel represents a virtual loudspeaker with a fixed and known position. Sounds are thus panned and mixed onto this multi-channel format using standard panning laws, and later on, the signal of each channel is filtered independently by the HRTF corresponding to the position of the associated virtual loudspeaker.

Figure 2 - Virtual loudspeaker representation where each channel is depicted as a virtual loudspeaker around the listener (i.e. the camera in a first-person shooter, the avatar in a third-person shooter). In a VR game, the signal of each virtual loudspeaker is passed through an HRTF corresponding to its position (fixed), for each ear of the headphones mix.
In fact, the virtual loudspeaker representation is not different from a classic multi-channel signal. The difference here is the context in which it is used. When mixing for a traditional 5.1 setup, sounds are panned and mixed directly onto a 5.1 bus and each channel of this bus is used to drive a physical loudspeaker. In our case, however, we are panning onto a configuration that purposefully has more channels than the output (which is two). The directional information implicitly conveyed in the virtual loudspeaker channels becomes embedded into the binaural signal by way of filtering.
In Wwise, you may implement this method by routing 3D sounds to an audio bus that is dedicated to the intermediate spatial representation, and you can have its parent perform the binaural rendering. In this case, the latter has the binaural Effect, and the former has mastering Effects (if desired).
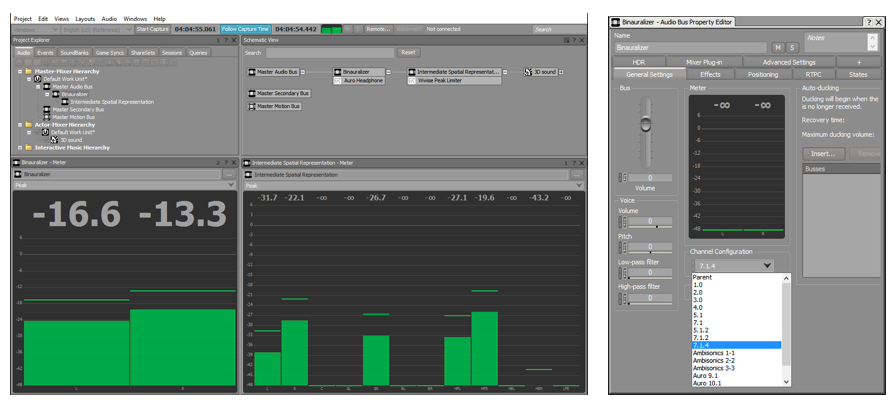
Click here to enlarge image (left) Click here to enlarge image (right)
Figure 3 - Using a virtual loudspeaker representation in Wwise, as illustrated in the Project Explorer and Schematic View. Both busses are set to a standard configuration with multiple speakers, such as 7.1.4. Height channels are required in order to represent sound coming from above the listener.
Ambisonics
We can view ambisonics as another intermediate spatial representation. Each channel carries a so-called spherical harmonic, and they all work together in approximating a sound field. First-order ambisonics consists of 4 channels, W, X, Y and Z (in FuMa convention). W is called the omni channel, and it carries the direction-agnostic signal. X, Y and Z carry direction-dependent audio in three main axes (front-back, left-right and top-down).
Higher-order ambisonics (HOA) is a bit trickier to illustrate, but we can interpret higher orders as carrying additional data that improves spatial precision. 2nd-, 3rd-, 4th- and 5th-order ambisonics consist of 9, 16, 25 and 36 channels respectively, and are therefore increasingly precise.
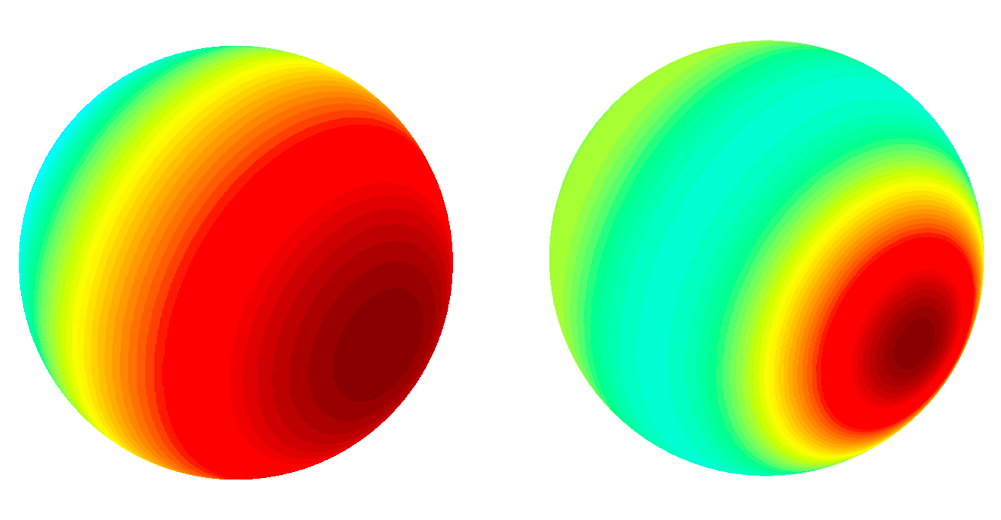
Figure 4 - Point source represented with 1st order ambisonics (left), 3rd order ambisonics (right). Color warmth is proportional to signal energy.
In ambisonic terminology, panning to ambisonics corresponds to encoding, while converting ambisonics to a binaural setup or a loudspeaker feed corresponds to decoding.
Unlike a typical virtual loudspeaker representation such as a 7.1.4 set up, ambisonics is symmetrical and regular in all directions and can represent sources coming from under the listener. However, ambisonics is more blurry than the virtual loudspeaker representation with an equal number of channels. Ambisonics will exhibit constant spread, and while amplitude panning over speakers can be more precise when a virtual source falls exactly on a speaker, it may not be if it falls exactly in the middle of three surrounding speakers.
Implementing ambisonics as an intermediate spatial representation in Wwise is as easy as the virtual loudspeaker methods. Just set the busses to an ambisonic configuration. Higher orders are recommended in order to obtain satisfying spatial precision.
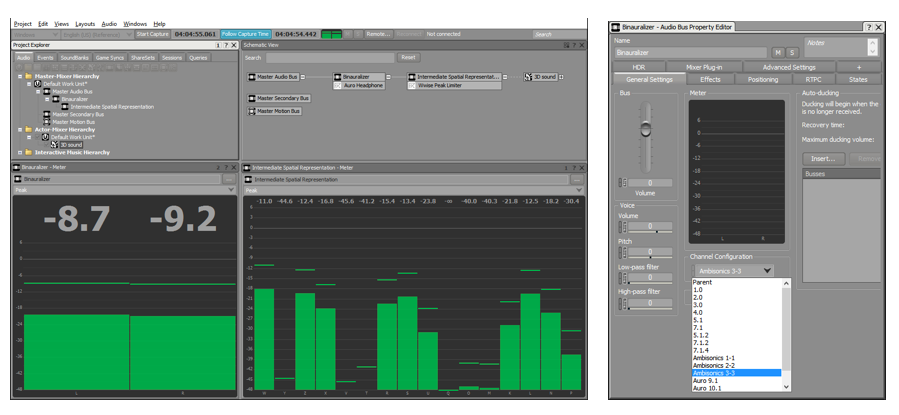
Click here to enlarge image (left)
Click here to enlarge image (right)
Figure 5 - Using an ambisonic intermediate spatial representation in Wwise, as illustrated in the Project Explorer and Schematic View. Both busses are set to an ambisonic configuration. Higher orders are recommended in order to obtain satisfying spatial precision.
At the moment, some VR vendors already provide SDKs that accept ambisonic signals and perform binaural virtualization. As they become available, Wwise will be capable of feeding these VR devices directly with ambisonics. Otherwise, it allows decoding ambisonics and converting to binaural using your favorite 3D audio plug-in. Auro Headphone, and Google Resonance, distributed with Wwise, are two examples.
Finally, another benefit of integrating the intermediate spatial representation in your workflow and using ambisonics for this purpose is that it can act as an exchange format.
Ambisonics beyond VR
We recently tried the same workflow at the SAT dome during the iX Symposium. Instead of decoding the ambisonics bus to a binaural feed, we used the Wwise default algorithm to decode to the actual loudspeaker setup of the dome, which consists of 31 clusters of loudspeakers.
We conducted an interesting experiment with the audience where we compared the resulting sound of a helicopter passing by over our heads using three different spatialization strategies:
- direct panning onto the 31 speakers;
- encoding to 3rd order ambisonics, then decoding to 31 speakers;
- encoding to 1st order ambisonics, then decoding to 31 speakers.
While using 1st order ambisonics resulted in a significantly "broader" image, the majority of attendees agreed that 3rd order ambisonics felt very comparable to the direct panning method in terms of precision.
Coming up next in this spatial audio blog series, we will explore how the ambisonic pipeline can be used for cinematic VR. So, stay tuned for more benefits and uses of the ambisonic pipeline.



Comments
Tommaso Perego
April 04, 2024 at 08:23 am
Hi Louis-Xavier I was wondering what could be the best procedure for setting up Wwise for using ambiences in 3D (Ambsionics 1st-3rd Order) and virtual sound source as audio objects to be heard as part of those ambisonics ambiences. According to what I understood from your article, I could do that with Wwise. Is there any video-instructions on how to set that up exactly?